Why do I see this?
Because of UiS's security policy, the GPU-website is only accessible from within the UiS network. You are trying to access the GPU-website from outside, and are therefore redirected to this site. If you want to access the GPU-website, please follow the instructions below.
How to access the GPU-website
If you do not have a Unix-account, register for one here:
http://user.ux.uis.no/Method 1 - NoMachine
You need to download the NoMachine client and configure it to connect to the Unix-network. Follow the instructions here:
http://nx.ux.uis.no/After installation and configuration, create a new virtual desktop. You can now open the firefox browser and access the GPU-website. Inside the virtual desktop, you can also open a terminal window and file browser with access to all your files.
Method 2 - Passwordless SSH Tunneling
SSH Tunneling is explained in detail here: SSH tunnel
This method works out-of-the-box on macOS and Linux. Windows users, however, must install bash (follow instructions here: How to Install Linux Bash Shell on Windows 10)
Step 1 - Create SSH Keys and copy to Unix-servers
Open a new terminal window on your local computer and run the command ssh-keygen to generate a private and public key (if you do not already have it). SSH keys are authentication credentials, just like passwords, and thus must be managed similarly.
The SSH Keys will be stored under ~/.ssh/ and consists of two files:
id_rsais your private keyid_rsa.pubis your public key
Next, we need to copy the public key to the Unix-server. Enter the command:
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa <your-unix-username>@ssh1.ux.uis.no
The command then asks for the password for your Unix-account. The -i argument lets us specify the path to our SSH Keys, the ssh-copy-id command will only copy the public key.
Step 2 - Create a SSH config file
Go to your local ssh folder with the command cd ~/.ssh/.
Use your favorite text editor to open/create the config file (for example, vim config).
Then add the text below in your ~/.ssh/config file. Remember to change the username.
Host uisHostName ssh1.ux.uis.noUser <your-unix-username>IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
You can also add ssh proxy setting in the same file to directly access the Gorina and Badne servers like this
Host badne* gorina*Hostname %h.ux.uis.noUser <your-unix-username>ProxyCommand ssh uis -W %h:%p 2> /dev/nullIdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsaNow you should be able to run the command ssh uis which should take you to ssh1.ux.uis.no without password or ssh gorina6 directly to gorina6 without a password.
Step 3 - Set up port forwarding
To create port forwarding (assuming you have followed above setup) run: ssh -D 8123 -f -C -q -N uis
Explanation of arguments
- -D 8123: Tells SSH that we want a SOCKS tunnel on the specified port number (you can choose a number between 1025-65536)
- -f: Forks the process to the background
- -C: Compresses the data before sending it
- -q: Uses quiet mode
- -N: Tells SSH that no command will be sent once the tunnel is up
Verify that the tunnel is up and running with this command: ps aux | grep ssh
You can quit your terminal application, and the tunnel will stay up. That is because we used the -f argument, which put the SSH session into the background.
Tip! To make things a bit easier, the command can be added as an alias. Open your .bashrc or .zshrc file, and add the following:
alias sshuistunnel=ssh -D 8123 -f -C -q -N uis
You will need to refresh the shell afterward by running the command source ~/.bash_profile or source ~/.zsh. You can also just restart your terminal to refresh the shell.
You can now simply run the command sshuistunnel, which will execute the command ssh -D 8123 -f -C -q -N uis.
Making aliases should be quite similar on each OS, but if you have any problems adding the command as an alias, see the links below for detailed instruction on your OS:
Make an Alias in Bash or Zsh Shell in macOS, OS X TerminalHow to Create and Use Alias Command in Linux
Create an alias in Ubuntu Bash on Windows
Terminating the tunnel. If you wish to terminate the tunnel, we need to identify the process ID (PID) using the ps command, and then kill it using the kill command. To search for all active ssh processes on the machine, use the command: ps aux | grep ssh. Find the line that looks like the command above. On that line, the first column is your username, and the second column is the PID. You can now simply terminate the tunnel with the command kill <PID>.
Step 4 - Configure Firefox
Once that is running, you can use Firefox browser to set the proxy.
Go to:
Firefox -> Options -> General -> Network settings
Set the manual proxy configuration and set the SOCKS v5 Host as shown in the image below. Do not forget to enable Proxy DNS when using SOCKS v5, or you can set up a system-wide proxy depending on your OS. Then you should be able to access gpu.ux.uis.no from outside of UiS.
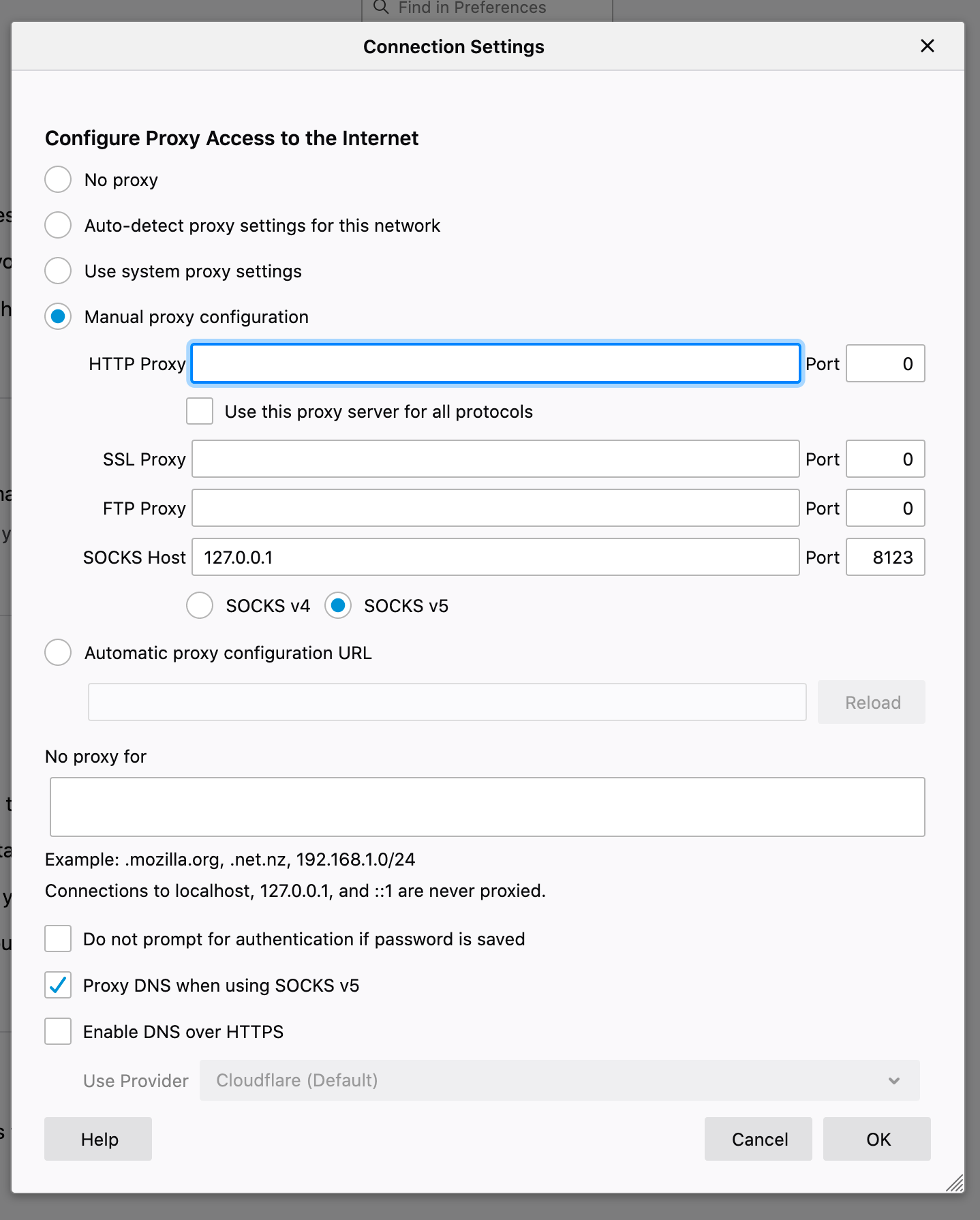
Tip Windows Users. If you are experiencing problems setting up an SSH tunnel using Firefox, try to add the socks proxy to the Internet Options in Control Panel (the old-school way of adding proxies to windows):
- Right-click start -> control panel -> internet options -> connections tab -> LAN settings
- Check off "Use a proxy server for your LAN..." -- Optionally, select "Bypass proxy server for local addresses"
- Choose "Advanced"
- Enter in the IP and port (127.0.0.1 : port) in the "Socks" fields, and leave the rest of them blank
- Hit OK to save/exit out
- Test with Internet Explorer browser